학사
-
[3학년][1학기][데이터마이닝][10w]2024.05.09
-
[3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][9W][2]2024.05.05
-
[3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][9W][1]2024.05.04
-
[3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][7w]2024.04.19
-
[3학년][1학기][인공지능시스템][7w]2024.04.17
-
[3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][7W]2024.04.16
-
[3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][과제] SMT20202024.04.10
-
[3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][5w]2024.04.05
[3학년][1학기][데이터마이닝][10w]



'학사 > 아주대 융시공' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [4학년][1학기][메타버스입문][W1] (0) | 2025.03.06 |
|---|---|
| [3학년][2학기][소셜네트워크분석][과제] 논문 리뷰 (6) | 2024.09.27 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][9W][2] (0) | 2024.05.05 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][9W][1] (0) | 2024.05.04 |
| [3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][7w] (0) | 2024.04.19 |
[3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][9W][2]
Bulk Metal Forming
Bulk Deformation
- Metal forming operations which cause significant shape change
- Starting forms: cylindrical bars and billets, rectangular billets and slabs, and similar shapes
Importance of Bulk Deformation
- In hot working, significant shape change can be accomplished
- In cold working, strength can be increased during shape change
- Little or no waste: some operations are near net shape or net shape processes
- The parts require little or no subsequent machining
Four Basic Bulk Deformation Processes
- Rolling: slab or plate is squeesed between opposing rolls
- Forging: work is squeezed and shaped between opposing dies
- Extrusion: work is squeezed through a die opening, thereby taking the shape of the opening
- Wire and bar drawing: diameter of wire or bar is reduced by pulling it through a die opening
Rolling
- which work thickness is reduced by compressive forces exerted by tow opposing rolls
The Rolls
- The rotating rolls perform two main functions
- Pull the work into the gap between them by friction between workpart and rolls
- Simultaneously squeeze the work to reduce cross section
Types of Rolling
- By geometry of work
- Flat rolling
- Draft: amount of thickness reduction
- d = t0 - tf
- Reduction: draft expressed as a fraction of starting stock thickness
- r = d / t0
- d = draft
- t0 = starting tthickness
- tf = final thickness
- Draft: amount of thickness reduction
- Shape rolling
- Work is deformed into a contoured cross-sectiion rather than flat
- Flat rolling
- By temperature of work
- Hot rolling
- Cold rolling
Rollling Mills
- Equipment is massive and expensive
- Two-high: two opposing large diameter rolls
- Three-high: work passes through both directions
- Four-high: backing rolls rupport smaller work rolls
- Cluster mill: multiple backing rolls on smaller rolls
- Tendem rolling mill: sequence of two-high mills
Thread Rolling
- Most important commercial process for mass producting bolts and screws
- Performed by cold working in thread rolling machines
- Advantages over thread cutting
- Higher production rates
- Better aterial utilization
- Stronger threads due to work hardening
- Better fatigue resistance due to compressive stresses introduced by rolling
Ring Rolling
- 언급만 잠깐 하고 넘어감
Forging
- Deformation process in which work is compressed between two dies
- Components: engine crangshafts, connecting rods, grears, aircraft structural components, jet engine turbine parts
Classification of Forging Operations
- Cold vs Hot forging
- Hot or warm forging: most common, due to the significant deformation and the need to reduce strength and increase ductility of work metal
- Cold forging: advantage is increased strength that results from strain hardening
- Impact vs press forging
- Forge hammer - applies an impact load
- Forge press - applies gradual pressure
Types of Forging Dies
- Open-die forging
- work is compressed between two flat dies, allowing metal to flow laterally without constraint
- Compression of workpart with cylindrical cross-section between two flat dies
- Impression-die forging
- die surfaces contain a cavity or impression that is imparted to workpart, thus constraining metal flow - flash is created
- Compression of workpart by dies with inverse of desired part shape
- Flash is formed by metal that flows beyond die cavity into small gap between die plates
- Flash must be later trimmed from part
- Flashless forging
- workpart is completely constrained in die and no excess flash is produced
- Compression of work in punch and die tooling whose cavity does allow for flash
- Starting workpart volume must equal die cavity volume within very close tolerance
- Process control more demanding than imporession-die forging
- Best suited to part geometries that are simple and symmetrical
- Often classified as a precision forging process
Impression-Die Forging Advantages and Limitations
- Advantages(compared to machining from solid storck)
- Higher production rates
- Conservation of metal(less waste)
- Greater strength
- Favorable grain orientation in the metal
- Limitations
- Not capable of close tolerances
- Machining often required to achieve accuracies and features needed, such as holes, threads, and mating surfaces that fit with other components
Forging Presses
- Apply gradual pressure to accomplish compression operation
- Mechanical presses: converts rotation of drive motor into linear motion of ram
- Hydraulic presses: hydraulic piston actuates ram
- Screw presses: screw mechanism drives ram
Upsetting and Heading
- Forging process used to form heads on nails, bolts, and similar hardware products
- Cycle
- wire stock is fed to the stop
- gripping dies close on the stock and the stop is retracted
- punch moves forward
- bottoms to form the head
Swaging
- Accomplished by rotating dies that hammer a workpiece radially inward to taper it as the piece is fed into the dies
Trimming
- Cutting operation to remove flash from workpart in impression-die forging
Digital Inspection System
- 비접촉식 Digital 형상 측정 기술을 통하여 실물로부터 CAD Data를 생성하거나 CAD Data와 생산품(부품, PP, 양산품 등) 간의 2/3D 기하학적 차이를 비교검증하는 기술
- 측정기를 활용하는 두 가지 기술
- Reverse Engineering
- 실물로부터 디지털화된 CAD Data 생성: 디지털 복제 기술
- 제품은 있는데 CAD Model 없음
- Inspection
- 기준 CAD Data와 실제품의 3차원 측정 데이터간의 신속 비교
- 2D/3D Metrology, Comparison
Extrusion
- Compression forming process in which the work metal is forced to flow through a die opening to produce a desired cross-sectional shape
- Two basic types of extrusion
- Direct extrusion
- Indirect extrusion
Direct Extrusion
- Also called forward extrusion
- This extra portion, called the butt, must be separated
Indirect Extrusion
- Also called backward extrusion and reverse extrusion
- Limitations of indirect extrusion are imposed by the lower rigidity of hollow ram and difficulty in supporting extruded product as it exits die
General Advantages of Extrusion
- Variety of shapes possible, expecially in hot extrusion
- Limitation: part cross-section must be uniform throughout length
- Grain structure and strength enhanced in cold and warm extrusion
- Close tolerances possible, especially in cold extrusion
- In some operations, little or no waste of material
Hot vs. Cold Extrusion
- Hot extrusion
- prior heating of billet to above its recrystallizaion temperature
- This reduces strength and increases ductility of the metal, permitting more size reductions and more complex shapes
- Cold extrusion
- generally used to produce discrete parts
- The term impact extrusion is used to indicate high speed cold extrusion
Extrusion Ratio
- Also called the reduction ratio
- rx = A0/Af(>1)
- rx = extrusion ratio
- A0 = cross-sectional area of the starting billet
- Af = final cross-sectional area of the extruded section
- Applies to both direct and indirect extrusion
Die Angle
- Low
- surface area is large, leading to increased friction at die-billet interface
- Higher friction results in larger ram force
- High
- more turbulence in metal flow during reduction
- Turbulence increases ram force required
- Optimum angle depends on work material, billet temperature, and lubrication
- Maximum die angle = 90
Orifice Shape of Extrusion Die
- Simplest cross section shape = circular die orifice
- Shape of die orifice affects ram pressure
- As cross-section becomes more complex, higher pressure and greater force are required(ex: heat sink)
Extrusion Presses
- Either horizontal or vertical
- Horizontal more common
- Extrusion presses
- Usually hydraulically driven, which is expecially suited to semi-continuous direct extrusion of long sections
- Mechanical drives
- Often used for cold extrusion of individual parts
Wire and Bar Drawing
- Cross-section of a bar, rod, or wire is reduced by pulling it through a die opening
- area reduction in drawing r
- r = (A0-Af)/A0
- A0 = orifinal area of work
- Af = final work
Wire Drawing vs. Bar Drawing
- Difference is stock size
- Bar: large diameter bar and rod stock
- Wire: small diameter stock - wire sizes down to 0.03mm(0.001 in.)are possible
Drawing Practive and Products
- Drawing practive
- Performed as cold working
- Used for round cross-sections
- Products
- Wire: electrical wire
- Rod stock for nails, screws, rivets, springs
- Bar stock: metal bars
Continuous Drawing
- Consisting of multiple draw dies separated by accumulating drums
Features of a Draw Die
- Entry region
- Approach
- Bearing surface
- Back relief
- Die materials
Preparation of the Work for Wire or Bar Drawing
- Annealing: to increase ductility of stock
- Cleaning: to prevent damage to work surface and draw die
- Pointing: to reduce diameter of starting end to allow insertion through draw die
'학사 > 아주대 융시공' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [3학년][2학기][소셜네트워크분석][과제] 논문 리뷰 (6) | 2024.09.27 |
|---|---|
| [3학년][1학기][데이터마이닝][10w] (0) | 2024.05.09 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][9W][1] (0) | 2024.05.04 |
| [3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][7w] (0) | 2024.04.19 |
| [3학년][1학기][인공지능시스템][7w] (0) | 2024.04.17 |
[3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][9W][1]
Metal Forming
Metal Forming
- The tool, usually colled a die, applies stresses that exceed yield strength of metal
Stresses in Metal Forming
- Stresses to plastically deform the metal are usually compressive
- However, some forming processes
- Stretch the metal(tensile stresses)
- Other bend the metal(tensile and compressive)
- Still others apply shear stresses
Material Properties in Metal Forming
- Desirable material properties
- Low yield strength & high ductility
- These properties are affected by temperature
- Ductility increases and yield strength decreases when work temperature is raised
- Other factors
- Straint rate(변형속도) and friction
Bulk Deformation Processes
- Characterized by significant deformations and massive shape changes
- “Bulk” refers to workparts with relatively low surface area-to-volume ratios
- Starting work shapes include cylindrical billets and rectangular bars
- Basic bulk deformation processes: rolling, forging, extrusion, drawing
Sheet Metalworking
- High surface area-to-volume ratio of staring metal
- Basic sheet metalwokring operations: bending, drawing, shearing
Temperature in Metal Foraming
- Any deformation operation can be accomplished with lower forces and power at elevated temperature
- Three Temperature range in metal forming:
- Cold
- Warm
- Hot working
Cold Working
- Performed at room temperature(보통 20도) or slightly above
- Important mass production operations
- Minimum or no machining usually required
- These operations are near net shape or net shape processes
Advantages of Cold Forming vs. Hot Working
- Better Accuracy, closer toleratnces
- Better surface finish
- Strain hardening(변형 강화) increases strength and hardness
- Grain flow during deformation can cause desirable directional Properties in product
- No heating of work required
Disadvantages of Cold Forming
- Higher forces and power required
- Surfaces of staring workpiece must be free of scale and dirt
- Ductility and strainhardening limit the amount of forming that can be done
Warm Working
- Performed at temperatures above room temperature but below recrystallization temperature
- Dividing line between cold working and warm working often expressed in terms of melting point:
- 0.3Tm, where Tm = melting point for metal(absolute temperature)
Advantages of Warm Working
- Lower forces and power than in cold working
- More intricate work geometries possible
- Need for annealing may be reduced or eliminated
How Working
- Deformation at temperature above recrystallization temperature
- Recrystallization temperature = about one-half of melting point on absolute scale
- In practive, hot working usually performed somewhat above 0.5Tm
- Metal continues to soften as temperature increases above 0.5Tm, engancing advantage of hot working above this level
Why Hot Working?
- Capability for substaintial plastic deformation
- Why?
- Strength coefficient is substantially less than at room temperature
- Strain hardening exponent is zero(theoretically) Ductility is significantly increased
Advantages of Hot Working vs. Cold Working
- Workpart shape can be significantly altered
- Lower forces and power required
- Metals that usually fracture in cold working can be hot formed
- Strength properties of product are generally isotropic
- No strengthening of part occurs from work hardening
- Advantageous in cases when part is to be subsequently processed by cold forming
Disadvantages of Hot Working
- Lower dimensional accuracy
- Higher total energy required(due to the thermal energy to heat the workpiece)
- Work surface oxidation, poorer surface finish
- Shorter tool life
Friction in Metal Forming
- In most metal forming processes, friction is undesirable
- Metal flow is retarted
- Forces and power are increased
- Wears tooling faster
- Friction and tool wear are more severe in hot woriking
Lubrication in Metal Forming
- Metalworking lubricants are applied to tool-work interface in many forming operations to reduce garmful effects of friction
- Benefits
- Reduces sticking, forces, power, tool wear
- Better surface finish
- Removes heat from the tooling
Considerations in Choosing a Lubricant
- Type of forming processes(rolling, forging, sheet metal drawing, etc.)
- Hot working or cold working
- Work material
- Chemical reactivity with tool and work metals
- Ease of application
- Cost
'학사 > 아주대 융시공' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [3학년][1학기][데이터마이닝][10w] (0) | 2024.05.09 |
|---|---|
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][9W][2] (0) | 2024.05.05 |
| [3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][7w] (0) | 2024.04.19 |
| [3학년][1학기][인공지능시스템][7w] (0) | 2024.04.17 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][7W] (0) | 2024.04.16 |
[3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][7w]
6장 정보입력 및 처리
정보표시
- 간접 감지 상황에서 인간공학이 설계과정에 적용됨
표시장치로 나타내는 정보의 종류
- 표시장치로 나타내는 정보에는 정적 정보와 동적 정보
- 정적정보는 시간 경과에 관계없이 고정
- 동적정보는 시간에 따라 계속 변화
- 정량적 정보, 정확한 숫자 파악, 변수의 정량적 값을 표시
- 정성적 정보, 경향이나 변화 파악: 변수의 가변적 일면을 표시
- 상태 정보, 여러 경우(정상-비정상 등) 중 어디 해당하는지 선택 개념, 정성적 정보기도 함
- 경고 및 신호 정보, 상태정보 중 특별히 경고를 위한 것, 일종의 상태 정보
- 식별 정보, 어떤 것인지 있는 그대로 확인하기 위한, 크게보면 상태정보지만 선택이 아닌 있는 그대로 확인
- 묘사정보, 배경과 중첩된 요소 파악
- 영숫자 및 기호 정보, 언어, 수치와 관련된 코드화 정보 표시
- 시간 위상 정보, 지속시간이나 간격을 조절한 신호(모스부호, 점멸등)
표시 양식의 선정
- 온기, 소리, 맛 등의 감각 종류를 감각 양식(modalities, 5가지 감각)이라고 함
- 정보 전달용 표시장치 선정 혹은 설계 시 적절한 감각 양식 선택 필요
시각과 청각 표현 용도 비교
청각 시각
| 메시지 단순 | 메시지 복잡 |
| 메시지 짧음 | 메시지 긺 |
| 나중에 다시 안 봐도 됨 | 여러번 봐야됨 |
| 메시지가 그때의 사건 다룸 | 메시지가 공간적 위치 다룸 |
| 메시지의 지시대로 즉시 행동 | 즉각 행동을 요구하는 메시지 아님 |
| 시각 장치가 너무 많음 | 청각 장치가 너무 많음 |
| 수용 위치가 너무 밝거나 암순응 필요 | 수용 위치에 소음 많음 |
| 계속 움직이며 일 함 | 한 자리에서 일 함 |
| 신호원이 소리일 때 | |
| 계속 변화하는 정보일 때 | |
| 말로 대답해야할 때 |
정보의 코드화
- 코드화: 원래의 자극 정보를 새로운 형태로 바꾸고 기호로 표시
- 코드화할 때는 여러 차원 사용
- 정보를 포함하는 자극차원의 효과는 자극을 식별하는 사람의 능력과 두가지 이상의 자극을 구별하는 능력에 달림
표시장치 설계 순서
- 전달 정보 종류 파악 → 자극 형태 따라 감각 양식 선택 → 표시 장치 선택 → 코딩 방법 → 차원 선택
코드화할 때 고려할 수 있는 사항들
절대적 판단과 상대적 판단
- 절대적 판단은 자극이 하나이므로 비교 불가, 사실은 기억 속에서 비교
- 상대적 판단은 두 가지 이상의 자극을 비교, 차원에 따라 상대적으로 구별
단일차원에서의 절대적 판단
- 매직넘버 7 +- 2
- 여러 차원에도 적용 (5~9)
- 감각기관의 한계보다는 기억의 한계 때문
- 시각적 코드화 방법
- 단일 숫자 10개, 문자 26개
- 색상 9개, 색-채도-명도 24개 이상
다차원에서의 절대적 판단
- 차원의 수는 많고 각 차원의 수준 수가 적을 때가 반대 경우보다 더 좋다
- 코드화에서 다차원 사용 시 서로 직교하거나 중복하는 경우 있음
- 모양과 색상이 직교 차원(독립): 빨간 원, 초록 원, 빨간 사각형, 초록 사각형
- 모양과 색상이 중복 차원: 원은 모두 초록, 사각형은 모두 빨강
- 한 차원의 값으로 다른 차원 값을 예측 가능
직교차원의 조합
- 차원이 직교하면 절대적 기준에서 식별 가능한 자극 수 증가
- 그 수는 각 차원의 별도 확인할 수 있는 자극 수를 곱한 것 보다는 적음
- 가능하면 다차원-직교로 만들어야 함
중복차원의 조합
- 차원을 중복 조합하면 단일 차원 사용 시보다 확인할 수 있는 수준 증가
- 그래도 직교적 코드일때가 더 구분 가능한 자극 수가 많음
좋은 코딩시스템의 특징
- 코드의 검출성
- 검출 가능해야 함
- ex) 지하 채광 장비에서 색깔 코드를 사용하면 검출성 낮음
- 검출성 측정을 위해 검출 시도회수의 일정 비율(50%) 이상을 검출 할 수 있는 자극의 하한값 설정
- 코드의 구별성
- 여러 신호를 구별 가능해야 함
- 코드 기호는 다른 코드 기호와 구별될 수 있어야 함
- 피실험자에게 기준 자극을 제시하고 다양한 다른 자극을 제시하며 기준 자극과 같은지 다른지 판단하게 함
- 이 차이를 차이역 또는 변별역이라 함
- 코드의 의미화
- 사용자에게 의미가 있는 코드 사용
- 개념 양립성에 관한 것
- 코드의 표준화
- 어떤 상황에서나 같은 것을 사용
- 양립성
- 다차원 코드의 사용
- 다차원 코드를 사용하면 코드 자극 수와 식별성 증가
- 차원수 많고 수준이 적은 코드 고려
- 작업의 특수 요건과 필요 코드 수에 따라 중복 또는 직교 사용 고려
양립성(제일 중요하다)
- 자극 및 응답이 인간의 예상과의 관계를 말함
- → 자극과 반응이 사람의 기대에 부합하는 정도
- 양립성이 클수록 정보처리에서 재코드화 과정이 적음
- 결과적으로 학습과 응답시간이 빨라짐, 오류 적어짐, 정신적 작업부하 감소
양립성의 종류
- 개념, 동작, 공간 3가지
- 네번째 양식 양립성이 추가됨
개념 양립성
- 코드와 기호가 사람들이 가지고 있는 개념과 얼마나 부합하는가
- 코드의 의미와 관련
동작 양립성
- 제어 장치의 움직임과 표시 장치로 나타낸 시스템의 응답이 잘 부합하는지
공간 양립성
- 제어 장치와 관련 표시 장치의 공간적 배열에 관한 것
양식 양립성
- 작업에 따라서 그에 알맞은 자극-응답 양식의 조합
- 음성작업에서 양립성이 가장 좋은 조합은 음성표현과 음성응답
- 공간작업에서는 시각표현과 수동응답
- A/S: 소리로 들려주고 음성 대답
- V/S: 보여주고 음성 대답
- A/M: 소리로 들려주고 손으로 조작(몸으로)
- V/M: 보여주고 손으로 조작(몸으로)
양립관계의 기원
- 어떤 상황에서 양립성 관계는 본질적: 오른쪽으로 가기 위해 핸들 오른쪽으로 돌림
- 다른 양립성 관계는 습관이나 문화와 관련된 특성에서 파생
'학사 > 아주대 융시공' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][9W][2] (0) | 2024.05.05 |
|---|---|
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][9W][1] (0) | 2024.05.04 |
| [3학년][1학기][인공지능시스템][7w] (0) | 2024.04.17 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][7W] (0) | 2024.04.16 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][과제] SMT2020 (0) | 2024.04.10 |
[3학년][1학기][인공지능시스템][7w]
Deep Learning
Deep Learning
- Neural network와 Machine Learning의 한 분야
- 심층신경망을 기반으로 하는 학습 방법
- 음성인식, 영상인식 등 패턴인식 등에서 좋은 성과
Deep Neural Network;DNN (심층신경망)
- 여러 개의 Hidden Layer를 가진 신경망 계열의 모델
- 다층 신경망의 특수한 경우, 기존은 3~4개의 Hidden Layer
- Layer의 수가 많은 신경망 구조
- Convolutional Neural Network(CNN): Layer 개수 많아지기 시작
- DNN의 배경: 80년대 중반 다층 퍼셉트론 연구 이후 침체기 → 프로세서 성능향상과 빅데이터로 학습 시작
DNN 탄생 배경
- 기존 신경망의 Hidden Layer의 개수를 늘려 좀 더 정교한 학습 필요해짐
- CPU, GPU 성능이 향상
- 병렬 분산처리 가능
- 학습을 통한 전처리 과정이 추가되어 효율 향상
- 빅데이터 학습 가능한 환경
- 기존 신경망
- 학습 데이터에서 직접 Feature 추출하여 입력으로 사용
- Feature Vector에 따라 학습 결과에 영향 줌
- 딥러닝
- 학습을 위해 필요한 특징 추출과 학습을 함께 수행
Convolutional Neural Network; CNN
- 합성곱 연산을 사용하는 합성곱 신경망
- Feature Map을 이용하여 학습
- 영상분석, 영상인식, 컴퓨터 비전 등
- Instant Segmentation
Recurrent Neural Network; RNN
- 순환신경망은 데이터에서 규칙적인 패턴을 인식
- 노드 간의 연결이 순환적 구조를 가지는 것이 특징
- 시간에 따라 변하는 특징을 가지는 데이터를 잘 처리
- LSTM과 혼합 사용
Restricted Boltzmann Machine; RBM
- 비지도 학습에 활용
- 입력에 대한 확률 분포를 학습할 수 있는 신경망
Deep Belief Network; DBN
- RBM을 여러 층으로 쌓아올린 구조
- 비지도 학습 가능
Generative Adversarial Network; GAN
- 생성적 적대 신경망
- 서로 경쟁하는 두 개의 신경망에 의해 구현
Issues in Deep Learning
Vanishing Gradient Problem
- Hidden Layer가 많아질수록 전달되는 오차의 크기가 줄어들어 학습이 되지 않는 현상
- 1보다 작은 오차를 계속 곱하면 점점 0으로 가까워짐, 컴퓨터 수치 연산에서 0에 가까워지다가 underflow 발생 가능
- Dropout, ReLU 사용으로 해결
Initializing Weights
- 신경망 성능에 영향 주는 요소
- 일반적으로 0에 가까운 random value 사용
- 개선된 가중치 초기화 방법 사용
- RBM을 학습시킨 결과 사용: unsupervised learning
- singular value decomposition을 통해 orthogonal matrix로 초기화
Overfitting
- 모델이 train data에 지나치게 학습된 상태
- training error는 낮으나 test error가 높음
- Regularization, Dropout, Batch normalization으로 완화
- Regularization: 가중치의 크기를 학습 모델 함수에 추가
- Dropout: 일정 확률로 노드를 무작위 선택하여 학습에 참여, mini batch마다 dropout할 노드를 새롭게 선택
- Mini-batch: 전체 학습 데이터를 일정 크기로 나눔, mini batch 단위로 학습
Regularization
- 데이터 확대: 데이터를 더 많이 수집하면 학습 모델의 일반화 성능 좋아짐
- 데이터 생성
- 충분히 많은 데이터를 수집하기 어려움
- 인위적으로 데이터를 확대 → 훈련 과정에서 데이터 변형, 데이터 회전 또는 warping
- Weight Decay 방식
'학사 > 아주대 융시공' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][9W][1] (0) | 2024.05.04 |
|---|---|
| [3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][7w] (0) | 2024.04.19 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][7W] (0) | 2024.04.16 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][과제] SMT2020 (0) | 2024.04.10 |
| [3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][5w] (0) | 2024.04.05 |
[3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][7W]
Casting
- Classification of solidification processes
- Metals
- Glassworking
- Polymers and PMCs
- Casting
- Steps
- Melt the metal
- Pour it into a mold
- Let it freeze
- Steps
- : Process in which molten metal flows by gravity or other force into a mold where it solidifies in the shape of the mold cavity
Capabilities and Advantages of Casting
- Can create complex part geometries
- Can create both external and internal shapes
- Some casting processes are net shape; others are near net shape
- Can produce very large parts
- Some casting methods are suited to mass production
Disadvantages of Casting
- Limitations on mechanical properties
- Poor dimensional accuracy and surface finish for some processes
- Safety hazards to workers due to hot molten metals
- Environmental problems
The Mold in Casting
- Contains cavity whose geometry determines part shape
- Actual size and shape of cavity must be slightly oversized to allow for shrinkage of metal during solidification and cooling
Two Categories of Casting Process
- Expendable mold processes: 석고, 회반죽
- Permanent mold processes: 내화물
Advantages and Disadvantages
- More intricate geometries are possible with expendable mold processes
- Part shapes in permanent mold processes are limited by the need to open mold
- Permanent mold processes are more economic in high production operations
Forming the Mold Cavity
- Mold cavity is formed by packing sand around a pattern, which gas the shape of the part
- When the pattern is removed, the ramaining cavity has desired shape of cast part
- The pattern is usually oversized to allow for shrinkage of metal as it solidifies and cools
- Sand for the mold is moist and contains a binder to maintain shape
Cores in the Mold Cavity
- The mold cavity provides the external surfaces of the cast part
- In addition a casting may have internal surfaces, determined by a core, places inside the mold cavity to define the interior geometry of part
Gating System
- Channel through which molten metal flows into cavity from outside of mold
- Consists of a downsprue, through which metal enters a runner leading to the main cavity
- At top of down sprue, a pouring cup is often used to minimize splash and turbulence as the metal flows into downsprue
Riser
- Reservoir in the mold which is a source of liquid metal to compensate for shrinkage during solidification
- The riser must be designed to freeze after the main casting in order to satisfy its function
- 의도적으로 main cavity보다 느리게 굳도록 design
- liquid metal을 보충
Heating the Metal
- The heat required is the sum of
- Heat to raise temperature to melting point
- Heat of fusion to convert from solid to liquid
- Heat to raise molten metal to desired tempreaure for pouring
Pouring the Molten Metal
- Factors that determine success
- Pouring temperature
- Pouring rate
- Turbulence
Chvorinov’s Rule
- TST: total solidification time
- TST =
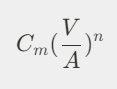
- V = Volume of the casting
- A = Surface area of casting
- n = exponent usually taken to have a value = 2
- C = mold constant
'학사 > 아주대 융시공' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][7w] (0) | 2024.04.19 |
|---|---|
| [3학년][1학기][인공지능시스템][7w] (0) | 2024.04.17 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][과제] SMT2020 (0) | 2024.04.10 |
| [3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][5w] (0) | 2024.04.05 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][5w] (0) | 2024.04.02 |
[3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][과제] SMT2020
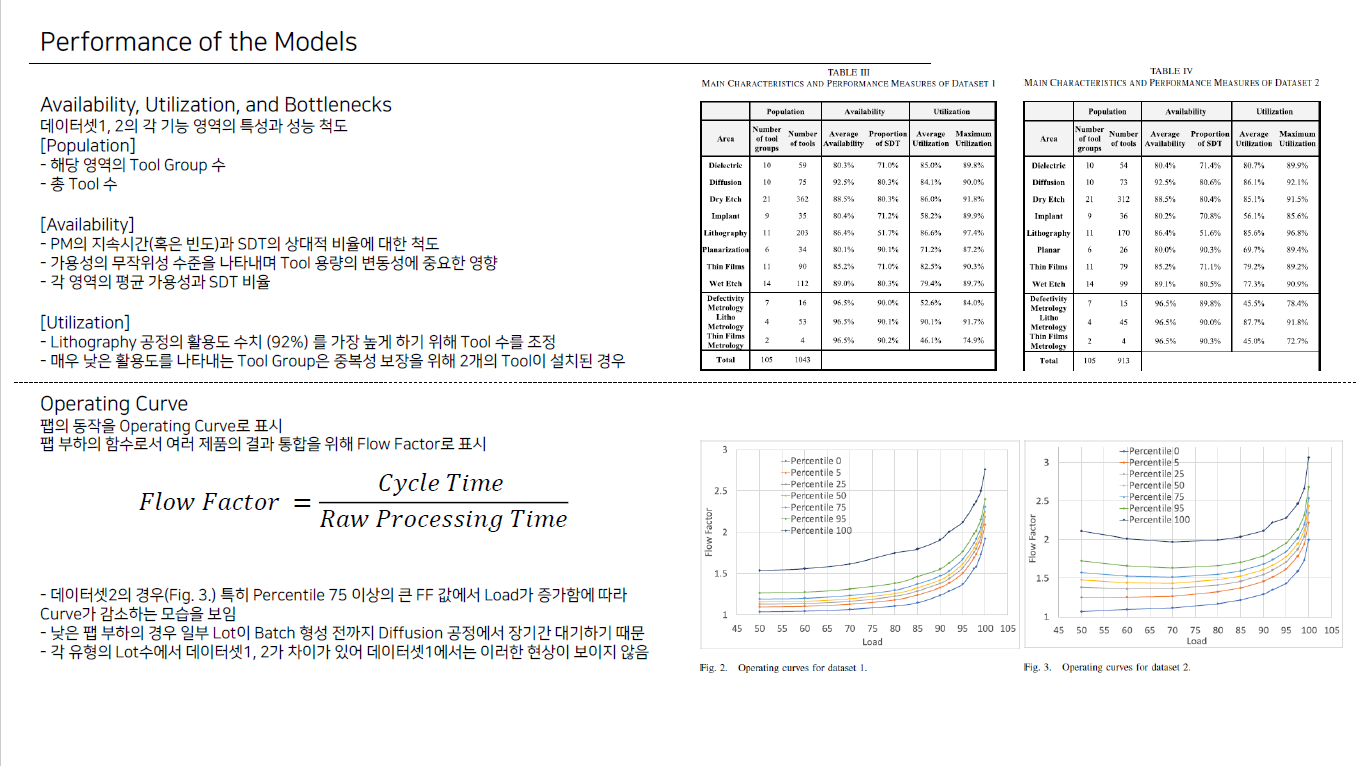
디지털제조입문 과제로 SMT2020 논문을 읽고 ppt 5장 분량으로 요약했다
논문 읽기는 좋아하지만, 시간제한이 있는건 싫고,
요약하는건 도움 될거라 생각하지만 반도체 fab 시뮬레이션 모델에 대해서는 큰 흥미가 없어요
그래도 어쨌든 열심히 한 과제니까
Denny Kopp, Michael Hassoun, Adar Kalir, Lars Monch,2020, SMT2020—A Semiconductor Manufacturing Testbed, IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing ( Volume: 33, Issue: 4, November 2020)
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9115710
SMT2020—A Semiconductor Manufacturing Testbed
We present a new set of simulation models, organized in a testbed. The aim of the testbed consists in providing researchers with a platform able to credibly represent the complexity of modern semiconductor manufacturing. The testbed is open to public use,
ieeexplore.ieee.org




'학사 > 아주대 융시공' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [3학년][1학기][인공지능시스템][7w] (0) | 2024.04.17 |
|---|---|
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][7W] (0) | 2024.04.16 |
| [3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][5w] (0) | 2024.04.05 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][5w] (0) | 2024.04.02 |
| [3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][4w] (1) | 2024.03.29 |
[3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][5w]
피부 감각
- 피부에는 다섯 가지 감각계통(피부감각 수용기)
- 촉점, 압적, 통점, 온점, 냉점
- 촉각적 표시장치에서는 대개 손과 손가락을 기본 정보 수용기로 이용
- 손은 위치에 따라 촉감이 다름
- 일반적 척도 중 하나인 2점역은 두 점을 눌렀을 때 각 지점을 따로 지각할 수 있는 두 점 사이의 최소 거리(청각의 JND)
- 손바닥, 손가락, 손가락 끝으로 갈 수록 감도가 증가(2점역이 감소)
- 세밀한 구별이 필요한 촉각적 표시장치는 손가락 끝을 사용하도록 설계
촉각적 표시장치
- 현재 주로 사용되는 촉각적 표시장치는 보는 것을 위한 시각장애인용과 듣는 것을 대체하는 청각장애인용
- 가장 자주 사용되는 자극유형은 기계적 진동이나 전기자극
- 진동 장치의 위치, 주파수, 세기, 지속시간과 같은 물리적 매개변수에 기초한 기계적 진동에 의해 정보 전달 가능
- 전기자극은 전극 위치, 펄스속도, 지속시간, 강도, 위상 등으로 코드화할 수 있음
시각 대체장치
- 인쇄물 판독
- 점자점의 위치, 점 사이의 거리, 크기를 달리하여 촉각으로 구별
- 문자와 숫자의 시각적 이미지를 시각장애인이 해석할 수 있는 촉각적 진동으로 변환할 수 있음
- 길 찾기 보조수단
- 촉각 지도는 정보 밀도를 낮춰야함(기호를 크게하고 간격을 두어야 촉각으로 확인 가능)
- 지도 위의 점, 선, 면적 등으로 구분
- 촉각 그래프
- 2차원 촉각 그래프
- 제어장치 식별
- 가장 실제적으로 촉각이 이용되는 것은 제어장치 손잡이와 관련된 설계
- 이러한 촉각 식별용 기구의 코드에는 모양, 감촉, 크기 등이 있음
청각 대체장치
- 듣는 것을 대체할 수 있는 촉각적 표시장치는 일반적으로 코드화된 메시지의 수용, 음성의 지각, 소리의 위치판단 등에 응용
- 코드 메시지의 수용
- 기계적 진동을 사용한 초기의 예
- 5가지 가슴 위치, 3가지 강도 수준, 3가지 지속시간을 사용하여 45종의 패턴 제작
- 문자 26개, 숫자 10개, 자주 쓰는 단어 4개를 코드화
- 음성의 지각
- 기계적, 전기적 자극을 통해 피부에 음성 전달
- 음의 위치 판단
- 귀에 설치한 마이크로 소리의 세기 측정, 마이크의 출력 증폭하여 사용자가 검지손가락을 대고 있는 두 진동장치에 보냄
후각
- 냄새 감각기인 후상피는 콧구멍 상부에 있는 작은 후세포
- 후세포에는 후모가 있으며 이것이 서로 다른 냄새를 검출
- 후각세포는 뇌의 후신경과 연결
- 콧구멍 → 후상피 → 후세포 → 후모 → 후신경
- 코듣 민감한 기관이지만 민감도는 특정 물질과 개인에 따라 다름
- 거짓경보율이 높음(false alarm rate), 아무 냄새 없는데 냄새가 난다고 할 때 많음
- 특정 냄새의 절대적 식별에 당면하면 후각은 그다지 우수하지 않음
- 훈련 받지 않은 피검자는 15~32종의 자극 구분, 훈련 받으면 60종까지
후각적 표시장치
- 후각적 표시장치는 다음과 같은 이유로 널리 응용되지 않음
- 사람마다 다양한 냄새에 대한 민감도 다름
- 코가 막히면 감도 떨어짐
- 빨리 냄새에 순응 → 잠시만 노출되어도 더이상 그 냄새 못 맡음
- 냄새의 확산 제어 어려움
- 어떤 냄새는 사람들이 싫어함
- 주로 경고용으로 유용
- 천연가스에 취기제(착취제)를 첨가하여 가스 누출을 검출 할 수 있게 함
음성 통신
- 음성은 청각정보 표시장치의 형태
음성의 성질
- 음성에 관계되는 기관은 폐, 후두, 인두, 입, 비강 등 여러가지
- 성대는 80~400회/sec로 아주 빨리 진동, 인두, 입 등을 통과하면서 진동수 증폭
음성의 종류
- 음성의 기본 단위는 음소, 단어의 의미를 변화시키는 음성의 최소 마디(모음과 자음)
- 음소가 모여서 음절이 되고, 음절이 모여 단어가 되고 이것이 문장을 구성
음성 묘사(표현)
- 음성을 비롯하여 소리의 공기 압력 변동을 그래프로 나타내는 여러 방법
- 파형은 시간에 따른 공기 압력의 세기 변동을 보임
- 스펙트럼은 임의 기간, 음소 또는 단어에 대하여 여러 주파수 별로 세기를 보임
- 음향분석도는 주파수를 수직축에, 시간을 수평축에 나타내고 세기를 명암의 정도로 묘사
음성의 세기
- 음성의 평균 세기 또는 음성파워는 아주 다양, 일반적으로 모음이 자음보다 음성파워가 큼
- 음성의 전반적인 세기는 사람마다 다름, 남성의 음성세기는 여성보다 3~5dB 정도 큼
- 조용히 말할 때 45dBA, 일상 대화에서 55dBA, 전화로 강의 65dBA, 고함과 유사 75dBA, 고함 85dBA
음성의 주파수 구성
- 일반적으로 남성은 여성보다 낮은 주파수 성분이 우세
음성 평가기준
- 음성통신시스템의 설계과정에서 의도하는 용도에 부합하는지를 평가하는 기준
- 주된 기준은 요해도이지만 음성품질도 포함
음성 요해도
- 요해도란 음성메시지를 정확하게 인지할 수 있는 정도
- 요해도 평가에서는 말을 들려주고 이를 따라하게 하거나 들려준 것에 관한 물음에 답하도록 함
- 일반적 상황에서는 문장이 요해도가 가장 좋고 개별 단어는 이보다 낮고, 무의미 음절이 가장 나쁨
음성 품질
- 음성품질은(또는 음성의 자연스러움) 요해도 이상으로 중요
- ex) 전화기 너머로 들려오는 말하는 사람의 신원을 인식하는 상황
- 음성품질은 선호도에 따라 정해짐
- 일반적으로 시스템을 통해 음성샘플을 들려주고 품질 등급을 매기게 하거나, 어떤 표준과 비교하여 선호하는 것을 고르도록 함
음성통신시스템의 구성
- 말하는 사람, 메시지, 전송시스템, 소음환경, 듣는 사람으로 구성
- 말하는 사람
- 음성 요해도는 말하는 사람의 목소리 특성에 따라서도 달라짐
- 우수한 발표자는 음절 지속기간이 길고 큰소리로 말하며 전체 발음 시간이 길고 쉬는 시간이 적으며 말할 때 기본적인 음성 주파수의 변화가 많음
- 적절한 말하기 연습을 하면 발표자의 요해도를 상당히 개선 가능
메시지
음소혼동
- DVPBDCET, FXSH, KJA, MN 등과 같은 부류의 문자는 서로 자주 혼동
- 일반적으로 소음이 있을 때는 단일 문자를 사용하지 말고 단어 철자 알파벳을 사용
단어 특성
- 일반적으로 짧은 단어보다는 긴 단어의 요해도가 큼
- 긴 단어는 일부만 알아들어도 전체 단어를 파악할 수 있음
문맥 특성
- 문장의 요해도가 개별 단어보다 좋은 것은 특정 단어를 알아듣지 못해도 문맥으로 정보 파악 가능하기 때문
- 의미가 있는 문장으로 배열하면 같은 문장을 무의미하게 나열했을 때보다 요해도 좋아짐
- 어휘에 다양한 단어를 사용할 수록 요해도 낮아짐(같은 의미의 단어를 여러 개 섞어 쓰면 안됨)
- 특히 소음 조건에서 메시지의 요해도를 개선하기 위해 설계할 때 다음 지침을 고려
- 어휘를 되도록 적게 사용
- 정보가 항상 같은 순서로 전달되도록 표준 문장 구조 사용
- 짧은 단어를 피하고, 개별 문자 대신에 단어 철자 알파벳 사용
- 수신자가 사용하는 단어와 문장구조에 친숙해지도록 함
전송시스템
- 음성전달시스템은 여러 형태로 왜곡될 수 있는데, 진폭왜곡, 주파수왜곡, 여과, 시간축 변조 등 → 음성 변조
- 진폭왜곡은 신호가 비선형 회로를 통과할 때 생기는 변형
- 이러한 왜곡 형태의 하나에 피크절단이 있음, 음성파의 피크가 절단되어 중앙 부분만 남음(낮음)
- 반면에 중앙절단은 주어진 값 이하의 진폭을 제거하여 음파의 피크를 남김(높음)
소음환경
- 소음은 외부 환경 소음이든 내부 소음이든 음성 요해도를 해침
- 소음이 음성통신에 미치는 영향을 평가하기 위한 가장 간단한 기법은 S/N비(신호 대 잡음 비)계산
- 잔향은 막힌 방의 벽, 천정, 바닥 등에서 소음이 울리는 효과
- 잔향도(특히 소음이 그친 후 60dB까지 감쇄되는 시간)으로 인한 요해도 감소
듣는 사람
- 청력이 정상, 수신하는 통신 유형에 훈련, 스트레스에 견뎌야 함, 여러 상충되는 자극 중에서 하나에 집중
- 듣는 사람의 나이도 요해도에 영향 미친
- 60세 이후로 요해도 감소, 말이 빠르고 군중 속에서 다른 목소리 존재, 잔향이 있을 때 현저히 요해도 감소
- 이러한 감소는 연령으로 인한 정상적 청력손실과 그동안 소음 환경에서 살았기 때문
- 귀마개나 귀덮개와 같은 청각보호수 착용 시에도 음성 요해도에 영향 미침
합성 음성
합성음성의 사용
- 많은 소비자 제품은 음성합성장치가 내장
- 어린이 장난감(교육용), 항공(조종석 경고용), 전화회사(안내용), 장애인을 돕기위한 합성 음성
음성합성법의 유형
- 전통적 방법은 테이프에 아날로그 신호로 기록했다가 재생
- 음성을 디지털화하여 컴퓨터 기억장치에 저장(전통적 방법의 발전)
- → 문제는 디지털화한 정보를 저장하기 위해 대규모 저장용량이 필요
- 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 분석합성법과 규칙합성법이 개발됨
분석합성법
- 사전에 코드화하거나 저장했던 단어나 문구만으로 음성메시지 만듦
- ex) book + case → bookase(발음상)
규칙합성법
- 진정한 합성 음성
- 기본 음성을 만드는 규칙, 기본 음성을 단어와 문장으로 조합하는 규칙, 특정 음이나 단어에 강세를 주어 말의 운율을 만드는 규칙에 집합에 기초하여 음성 만듦
- 장점은 비교적 적은 컴퓨터 용량을 사용하여 아주 많은 어휘가 가능, 인간 음성 없이도 새로운 어휘 만들 수 있음
- 문제는 음성의 질이 디지털화 음성에 기초한 방법만큼 좋지는 않음(요즘엔 아님, 이 내용 지워도 됨)
합성음성을 사용한 성능
- 합성음성 요해도
- : 합성음성의 요해도는 자연음성일 때보다 나쁨, 기술이 발달해서 거의 비슷함
- 합성음성 기억
- 사람들은 자연음성보다는 합성음성으로 말한 메시지를 잘 기억하지 못함
- 일반적으로 합성음성을 들을 때는 자연음성일 때보다 처리 용량이 더 필요
- 그러나 일단 코드화하면 합성음성도 자연음성과 마찬가지로 효과적으로 저장됨
합성음성 사용지침
- 음성 경고는 다른 음성과 정성적으로 달라야함
- 요해도를 최대화
- 가능하면 자연스럽게
- 재생모드를 설치하여 필요에 따라 사용자가 메시지를 재생할 수 있도록
- 사용자가 메시지를 중단할 수 있는 기능 제공 → 매번 들을 필요 없는 유경험자에게는 아주 중요
- 사용자가 시스템 음성에 친숙해지게하기 위해 소개 메시지나 훈련 메시지를 마련
'학사 > 아주대 융시공' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][7W] (0) | 2024.04.16 |
|---|---|
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][과제] SMT2020 (0) | 2024.04.10 |
| [3학년][1학기][디지털제조입문][5w] (0) | 2024.04.02 |
| [3학년][1학기][인간공학개론][4w] (1) | 2024.03.29 |
| [3학년][1학기][데이터마이닝][4w] (0) | 2024.03.27 |